transformer has been commonly used in recommendation system and it is the key building block to model sequence. however, transformer is very expensive. the computational cost of transformer is n^2 * d + n * d^2, where n represents the sequence length, for social media platform, it is easy build a sequence with potentially hundreds of actions, so a sequence of length 1K immediately will turn into a 1M operations.
Where this 1M comes from is during the self attention when calculating the attention scores QK_t.
Q: n * d, K: n * d => Q @ K_t = (n * d) @ (n * d)T = n ^ 2.
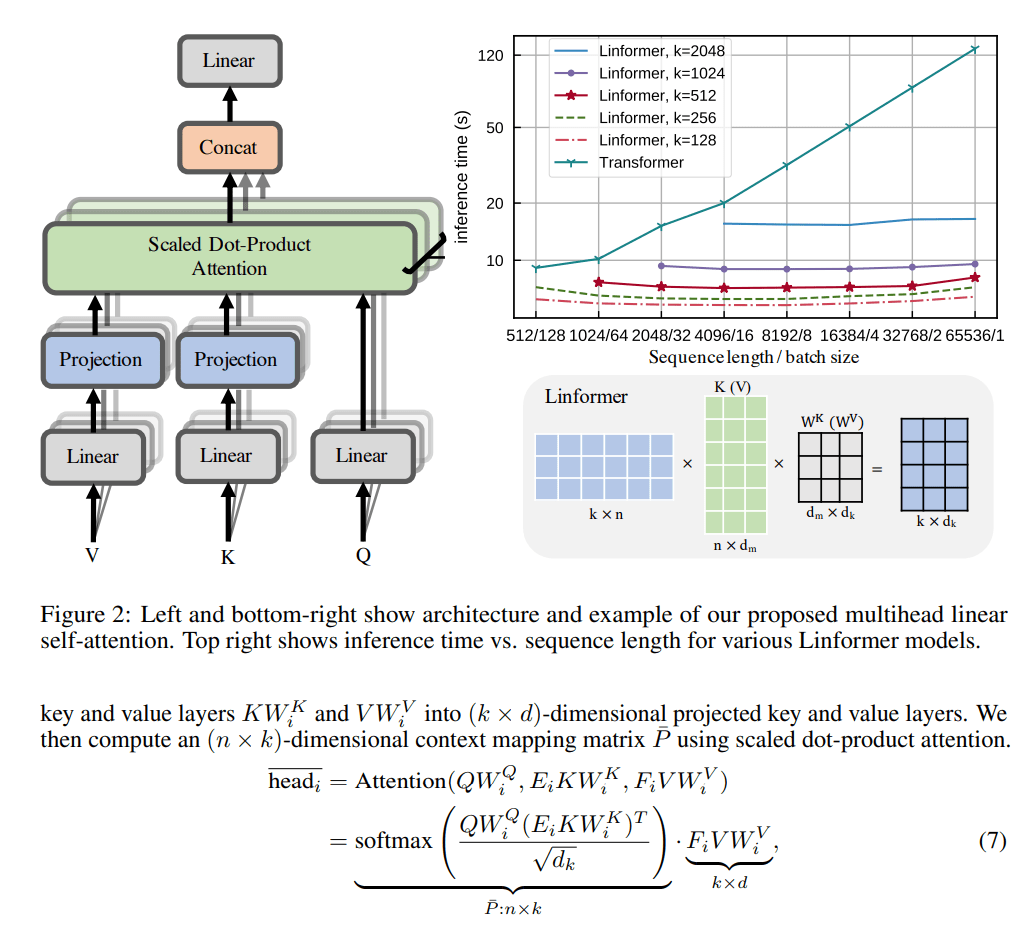
To avoid this from happening, researchers found that matrix are low rank matrices, which means by dimension reduction, we can project these matrices smaller matrices that will have a fixed dimension of r instead of n.
def linformer_attention(Q, K, V, E_K, E_V):
# Q: (n, d_k)
# K, V: (n, d_k)
# E_K, E_V: (n, r)
K_proj = E_K.T @ K # (r, d_k)
V_proj = E_V.T @ V # (r, d_k)
scores = (Q @ K_proj.T) / sqrt(d_k) # (n, r)
attn = softmax(scores, dim=-1) # (n, r)
out = attn @ V_proj # (n, d_k)
return out
In this psuedo code, we notice the attention score matrix is now n by r that grow linear with the sequence. In the very end, when we multiple with the value matrix, the dimension of r cancels out and we keep the final output exactly the same as the vanilla matrix. If we pick r to be 100 when n = 1000, using linformer will reduce the computation complexity by 10x.
Reference:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.04768