Today I was following the Apache HBase documentation, nowadays rebranded to be Apache HBase Book. It was a really good documentation but like any other documentation, I ran into a few typos in the documentation which I would love to be fixed.
Then I quickly noticed that there is actually a section in the documentation regarding how you should report an issue in the JIRA system and at the same time, you can assign the ticket to yourself, DIY and potentially integrate into the master branch.
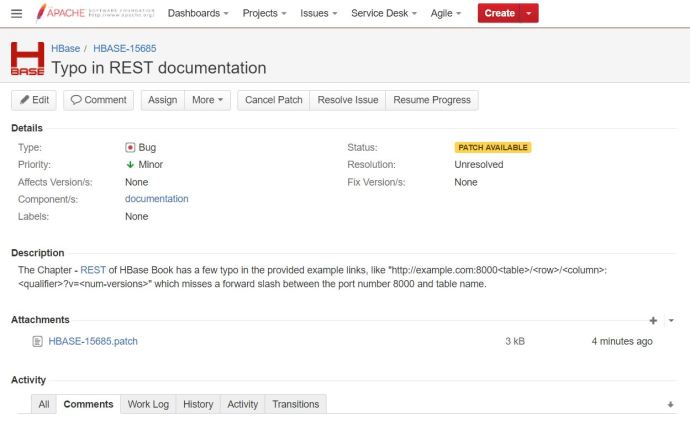
Here is a ticket that I have created regarding a few typos in the REST chapter in the book where a few forward slashes are missing between the port and table name. Then a guy asked me do I have my patch, ok, so the first question is “what on earth is a patch?” 🙂
After carefully reading this documentation, I realize that it is a fork, a changed version of the Apache HBase source code. Then I started the journey of following the suggested workflows trying to get my first patch.
The first step is to git clone the master branch of HBase source code, it is nothing more complex than copy a link from github and run a git clone command anywhere on your local file system. That process was pretty time consuming for the first time. It almost took me around 5 minutes to download 228MB source code to the Ubuntu VM that is running on my Windows gaming machine.
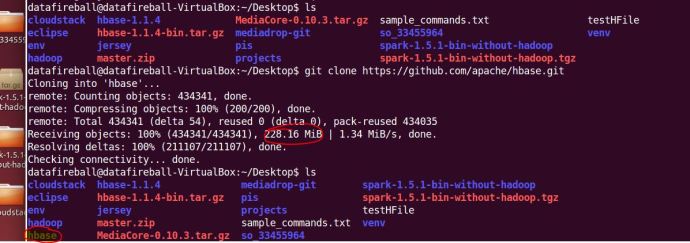
After downloading all the files, I took a quick look at the source code and realize one can easily get lost there and it will be really hard to locate what you want, even the folder where contains the source code of the HBase book.
I did a quick Google search and a grep command really helped me out locating where the REST chapter is located in the source code. I took a slice of a fairly unique text in the REST chapter and hopefully loop through all the files and locate the one that contains it, which supposed to be the file that I need to edit.
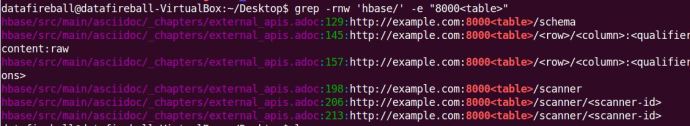
Now, one can easily tell that the REST section is located in a file that is under the hbase/src/main/asciidoc folder. Inside that folder, there are a folder for each chapter and the one that I am interested in under the external_apis.adoc file.
Hoorey! The moment I opened up this file, I realized it is another thing that I have to learn because this documentation is using a slight different text document format called “asciidoc“. I am amazed at how powerful, or how complex this whole asciidoc syntax is but my first reaction is. I pulled up the web version of the book and put it side by side with the asciidoc and it should help you quickly have an idea what ASCIIdoc is.
I have a question that why not use something that is more mainstream or straighforward like Markdown or Latex, but anyway, it is another day thing and lets fix our problem first.
It is not a rocket science project to really add in 6 slashes to the right place :), I quickly did that and did a git add and git commit with a commitment message.
Going through the checklist one by one, it says “If you have made documentation changes, be sure the documentation and website builds by running mvn clean site.”
I then switch back to the home directory of HBase and run mvn clean site with the “.” (dot). However, it gave me an build failure error after two minutes and then I reran the command mvn clean site without the dot. I learned from maven’s website that we have three stages in the lifecycle of a project, deployment, clean and site which I guess the mvn clean site is just to make sure we are in a good shape.
And then again, it took me ONE hour to run into another problem:
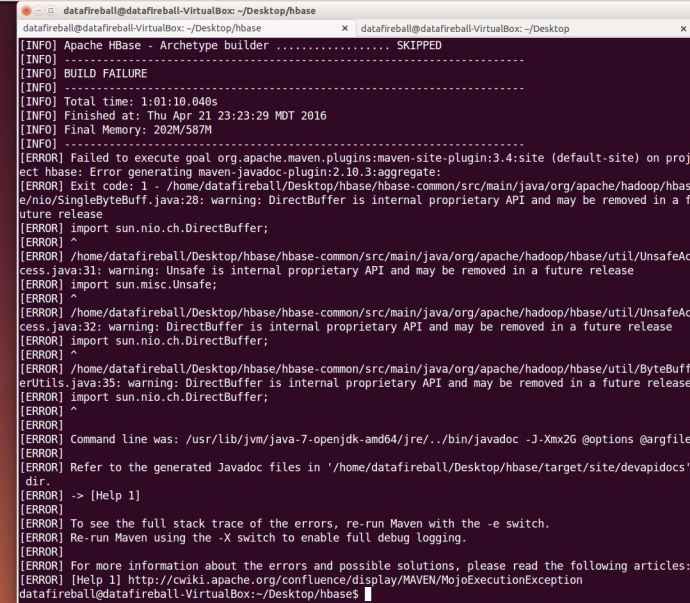
I am so surprised that I have only changed a few slashes but there problems i constantly ran into, I have a concern that it might just be the build environment that I have which is different comparing with the build system that HBase is using. in this case, I will simply assume it is a correct fix and add a patch.
The patch is simply a delta/diff file that shows what you have changed and what is different.
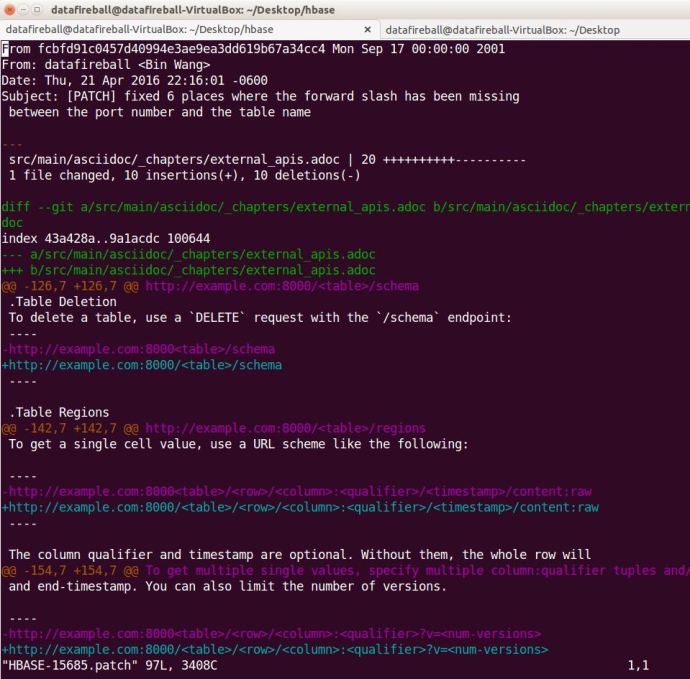
After following a tutorial, I attached that patch file to the JIRA ticket and it changed the status to “Patch Available” which I assume people will review and let me know if I made it or not.
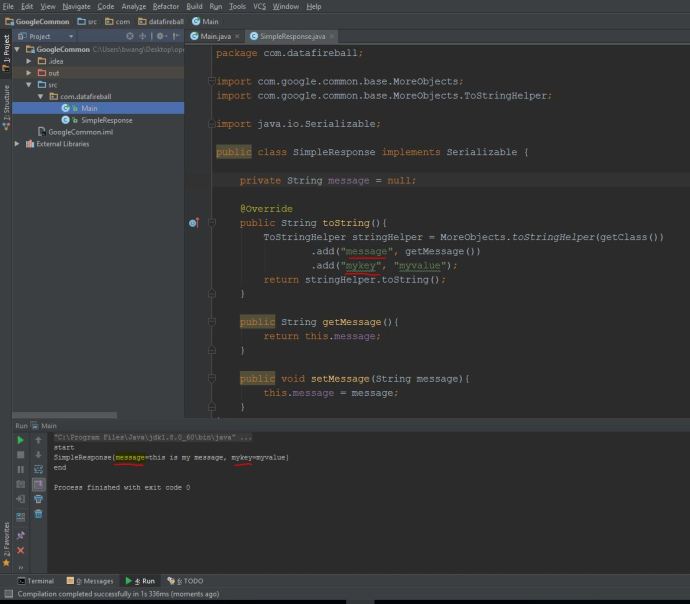
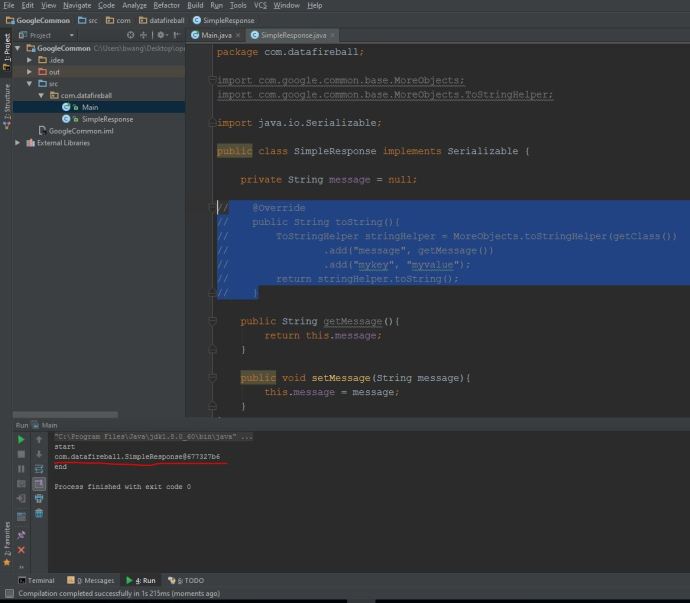
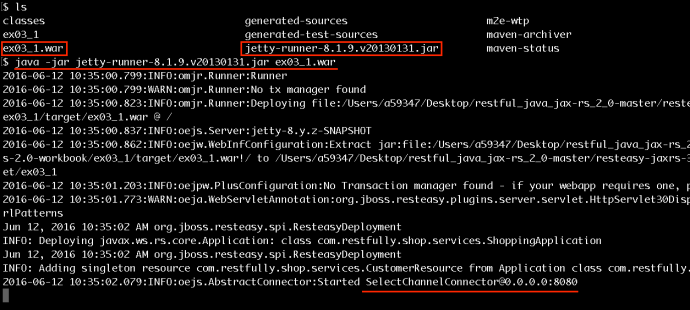
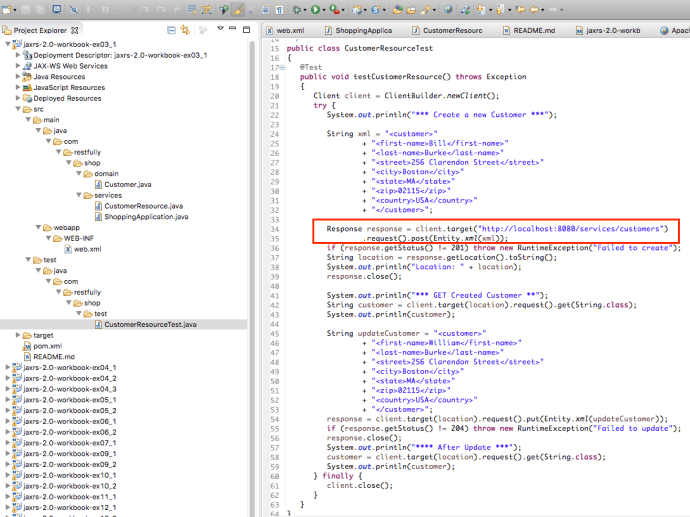
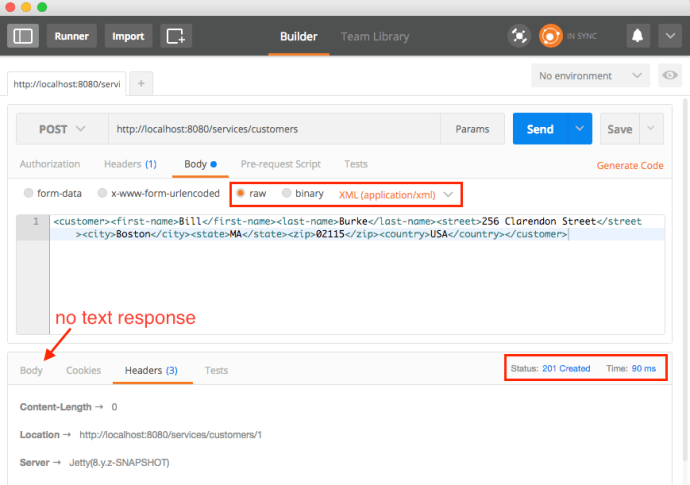
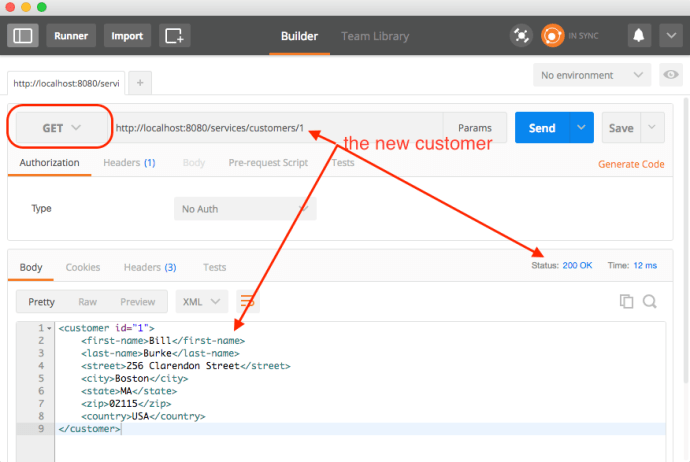
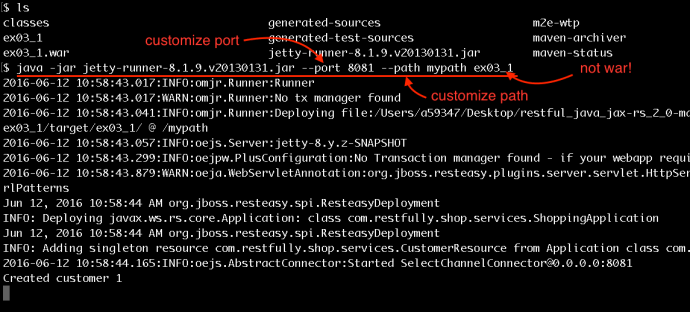
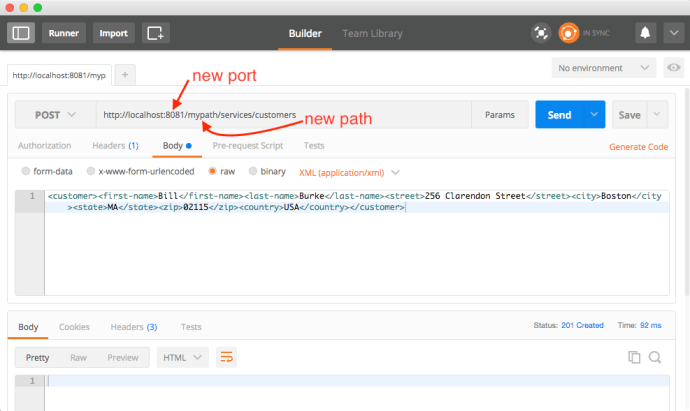
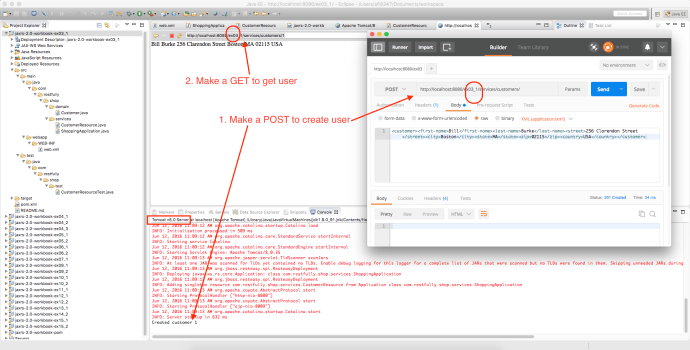
 As you can see, it “looks like” the application is working fine, however, after the maven build, it will not keep a server running and you really cannot have a hands-on experience playing around with the app. In that case, we need to deploy the application and keep it running as long as we want. And potentially test it using your own tool set instead that Junit test.
As you can see, it “looks like” the application is working fine, however, after the maven build, it will not keep a server running and you really cannot have a hands-on experience playing around with the app. In that case, we need to deploy the application and keep it running as long as we want. And potentially test it using your own tool set instead that Junit test.