In the data booming age, there is an unprecedented amount of demand for data processing, especially “big data scale” processing, something that you just know it won’t work on your laptop. A few common cases like parsing large amounts of HTML pages, preprocess millions of photos and many others. There are tools readily available if your data is fairly structured, like Hive, Impala but there are just those cases, which you need a bit more flexibility other than plain SQL. In this blog post, we will use one of the most popular frameworks Apache Spark, and share how to ship out your own Python environment without worrying at all about the Python dependency issues.
In most of the vanilla big data environment, HDFS is the still a common technology where data is stored. In Cloudera/Hortonworks distribution and cloud provider solutions like AWS EMR, they mostly YARN or Hadoop Next Gen. Even for an environment where Spark is installed, there are many users run Spark on top of YARN like this. As Python is the most commonly use language, Pyspark sounds like the best option.
Managing Python environment on your own laptop is already fun, managing multiple versions, multiple copies on a cluster that likely be shared with other users could be a disaster. If not otherwise configured, pySpark will use the default Python installed on each node. And your system admin certainly won’t let you mess with the server Python interpreter at all. So your cluster admin and you might come to a middle ground which a new Python, say Anaconda Python, can be installed on all the nodes using a network shared file system which you have more flexibility, as any installation can be mirrored to other nodes and the consistency is ensured. However, only after a few days that you noticed your colleagues accidentally “broke” the environment by upgrading certain libraries without you knowing, and now, you have to police that Python environment. After all, this comes to the question of how each user can customize their own Python environment and make sure it runs on the cluster. The answer to Python environment management is certainly Anaconda, and the answer to distributed shipment will be YARN archives argument.
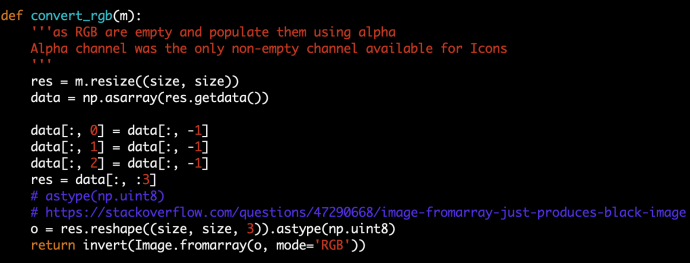
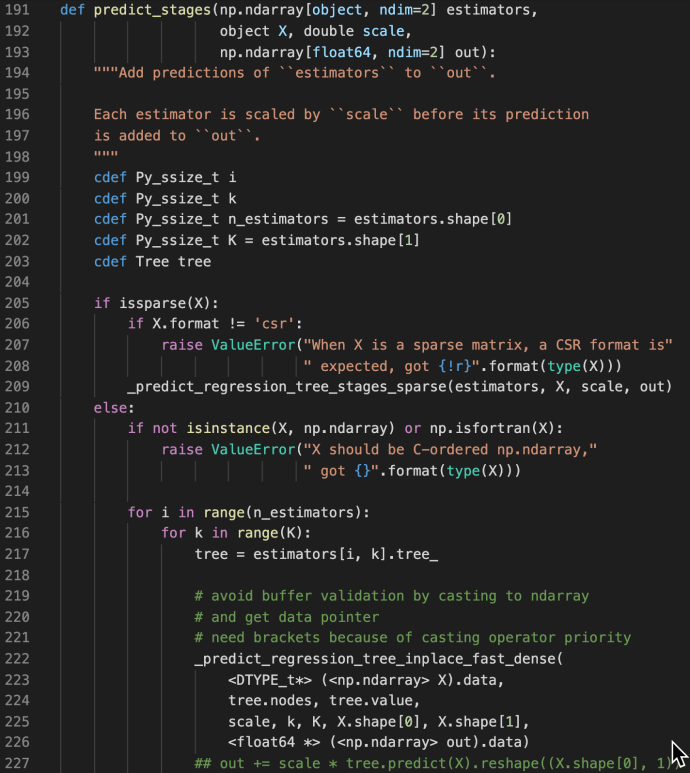
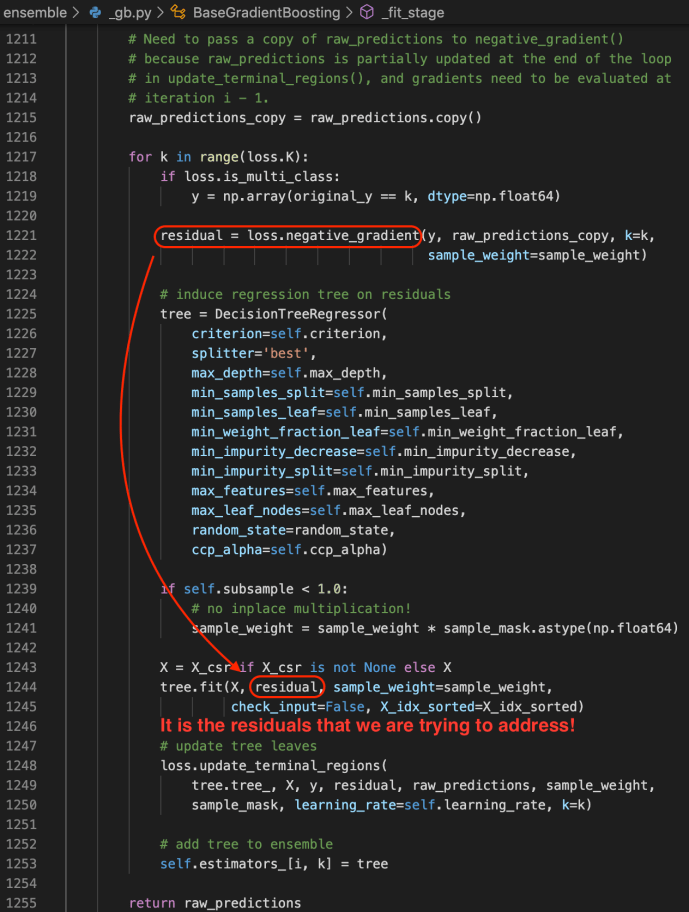
The idea is that for any project, feel free to create your own conda environment and do the development within that environment, so in the end, you will use the Python at your own choice and a clean environment with all the necessary libraries only installed for this project. Like a uber jar idea of Java. Everything python related in one box. Then, we will submit our pyspark job first by shipping that environment to all the executors where the workload will be distributed, but then second, configuring each executor will use the Python that we shipped. All the resource management, fan out and pull back will be handled by Spark and YARN. So three steps in total, first being a conda environment, second being a Pyspark driver and last is the code submition.
In the following section, I will share how to distribute the HTML parsing in a Cloudera environment as an example, every single step is also available on Github in case you want to follow along.
Conda
If you are not already familiar with Conda, it is only one of the tools that many Python users live and breathe on a day to day basis. You can learn more about Anaconda from here.
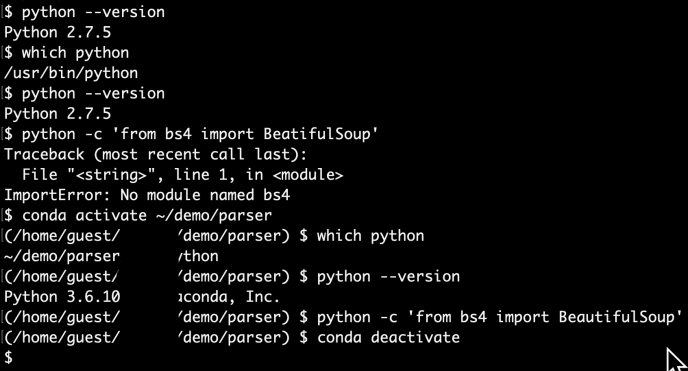
Driver.py
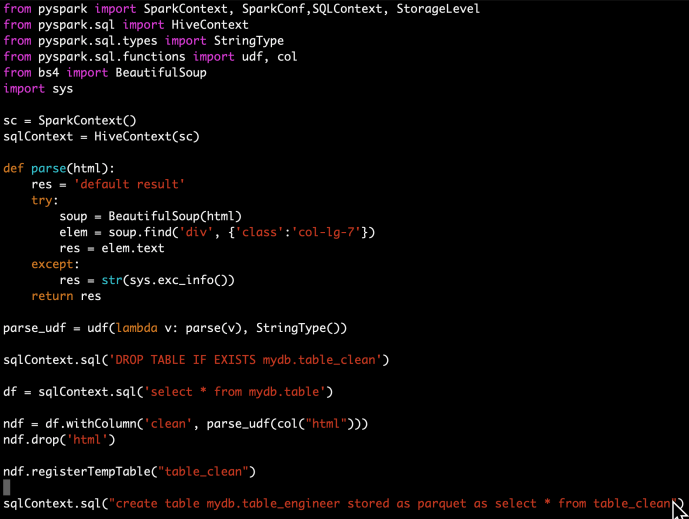
Run.sh

Reference:
[1] https://docs.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/5-14-x/topics/spark_python.html
[2] https://blog.cloudera.com/making-python-on-apache-hadoop-easier-with-anaconda-and-cdh/